Blockchain in the automotive industry
Blockchain was first known primarily as the technology behind crypto currencies. But more and more car manufacturers and suppliers are also seeing the benefits of this technology. After all, Blockchain can provide reliability, transparency and security throughout the chain: from raw material to recycling and customer relations.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is essentially a digital chain of blocks of information. Each block contains data linked to the previous block, creating a chronological and immutable chain. Imagine a digital ledger not owned by one party, but shared by thousands of computers simultaneously. Every addition is automatically recorded, checked and secured – all by the network itself. This makes modification, fraud and manipulation virtually impossible.
A blockchain can contain all kinds of information: financial transactions, production data, logistics data or customer information. Especially in a complex industry like the auto industry, where numerous links must work together, such a system can be particularly valuable.
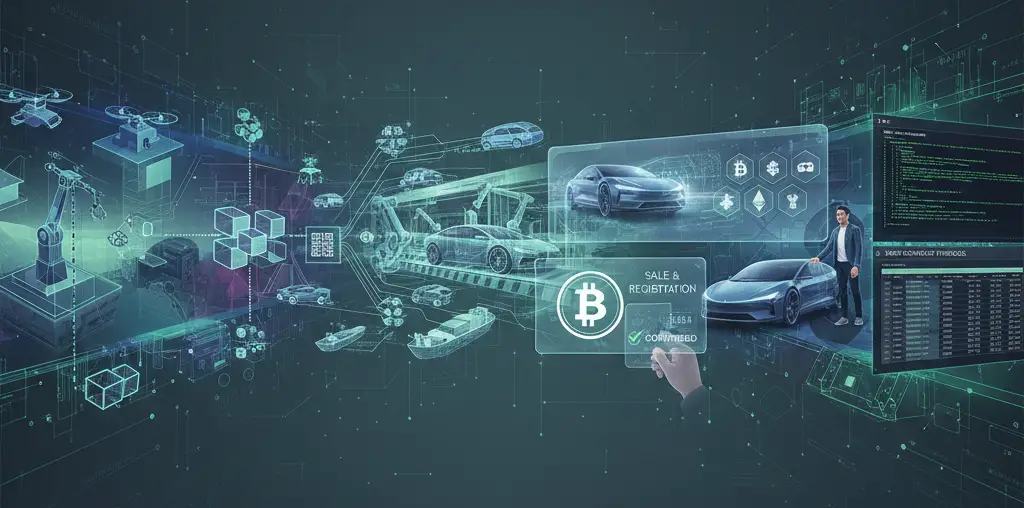
Blockchain in the automotive supply chain: from raw material to end user
Extraction of raw materials
Cars consist of thousands of parts made of numerous materials, such as steel, aluminum, lithium for batteries and rare metals. The origin story of these raw materials is sometimes sensitive and often difficult to verify. Blockchain can help record exactly where raw materials come from, how they were extracted and whether it was done in a sustainable and ethical way. This increases transparency and helps brands demonstrate that their supply chain is clean and fair.
Logistics and supply chain
The supply of materials and distribution of parts are crucial. Through blockchain, every shipment can be accurately tracked: from the mine or factory to the production line. Everyone in the chain can check in real time where a delivery is, whether the paperwork is correct and whether there are any discrepancies. This reduces the chance of errors and delays.
Production Process
During the production of a car, thousands of operations are performed. Blockchain can capture data about every part and step automatically. Think quality checks, production standards and software updates. This creates a complete digital record of the car. Should there be a problem later, such as a recall, it is immediately clear which cars are affected and which are not.
Sales and registration
When the car leaves the factory and heads toward the dealer, blockchain can again play a role. Sales records can be recorded on the blockchain, including ownership transfer and vehicle details. This prevents fraud, such as reversing mileage or falsifying documents. Insurance companies and governments can also follow along, making procedures faster and more reliable.
Financing, insurance and crypto payments
The sale of cars often involves financial constructions: loans, leases and insurance. Through blockchain, these processes can be automated and transparent. Smart contracts, called smart contracts, ensure that agreements are automatically executed as soon as conditions are met.
Some dealers or manufacturers, by the way, already accept payments in cryptocurrency. Thanks to blockchain, those transactions are fast and secure. A digital wallet (e-wallet) can also be linked to the car itself. Thus, in the future, you can use your car itself to pay for toll roads, parking or battery charging.
Maintenance and customer relationship
A major advantage of blockchain is that a car’s maintenance record can be securely and completely recorded. Every service, repair or software update enters the blockchain. For the buyer of a used car, this means security: you know exactly what happened to the car.
For manufacturers and dealers, it offers opportunities to build long-term customer relationships. Customers get reliable information through blockchain, while brands protect their reputation from fraud or counterfeiting.
Blockchain and smart cars
The rise of connected cars and autonomous driving requires huge amounts of data to be shared and processed in real time. Blockchain can play a key role here. Autonomous vehicles need to communicate with each other to prevent accidents. Blockchain can ensure that that communication is secure and cannot be manipulated. Payments between vehicles and infrastructure – think of a self-driving cab that automatically pays for a ride – can also be arranged via blockchain.
Is blockchain secure?
One of the biggest advantages of blockchain is security. Because data is stored scattered across a network rather than on one central server, hacking is much more difficult. Any change must be approved by the network. This makes blockchain very suitable at a time when cybercrime is on the rise and digital security is a top priority.
Yet blockchain is not invulnerable. Smart contracts can contain errors and cryptowallets can be hacked. Therefore, continuous development and monitoring is needed to keep the technology secure.
Will blockchain become the norm?
The question is whether blockchain will become the standard in the auto industry. Many car manufacturers are already experimenting with pilots, for example for resource tracking or maintenance logging, think major players such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz and Toyota.
Yet it will take time before blockchain is widely adopted. It requires cooperation between numerous parties: from mining companies to insurers. It also requires investments in technology and knowledge. Experts expect blockchain to become increasingly integrated over the next 10 to 15 years, but full standardization is likely to take longer.
Consumer implications
For consumers, blockchain can offer many benefits. You buy a car whose history is fully and reliably recorded. You can be confident that mileage and maintenance records are really correct. Payment can be faster and easier, perhaps even directly from the car.
There are also drawbacks. Blockchain is still relatively new and complex. Not every consumer will understand or trust the technology. In addition, digitization always brings questions about privacy and data use. Manufacturers and dealers must remain transparent in how they use data.
Conclusion: blockchain can add value
Blockchain can fundamentally change the auto industry. It offers solutions to problems that have existed for years: fraud, unclear origin of materials, unreliable mileage and inefficient processes. From mining to customer relations, blockchain can add value in every step of the chain.
Whether blockchain actually becomes the standard depends on cooperation among manufacturers, governments, dealers and consumers. What is certain is that the technology offers great opportunities to make the auto industry safer, more transparent and more efficient. For consumers, it means more security and convenience, although it remains important to look critically at how brands handle your data.
With blockchain, the car of the future will not only be electric and smart, but also reliable and transparent – from first screw to last mile.


